
With a deep commitment to your well-being, our approach is backed by training and experience, ensuring you receive the care you deserve. Explore how to address treatment for chronic depression and discover a path to reclaiming a fulfilling life. Your journey to healing starts here.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Dysthymia?
Persistent depressive disorder, or dysthymia, is a disorder characterized by low mood and hopelessness that lasts for a prolonged period. Compared to major depressive disorder (MDD), dysthymia involves more persistent but less severe symptoms of depression. Persistent depressive disorder is now in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM-5) as a combination of what used to be chronic major depressive disorder and dysthymic disorder.
Symptoms of dysthymia include:
- Depressed mood for most of the day for at least 2 years
- Feelings of hopelessness
- Poor appetite or overeating
- Trouble sleeping or sleeping too much
- Low energy
- Low self-esteem
- Poor concentration
To be diagnosed with dysthymia, the individual must not be without symptoms for more than 2 months at a time.
What Causes Dysthymia?
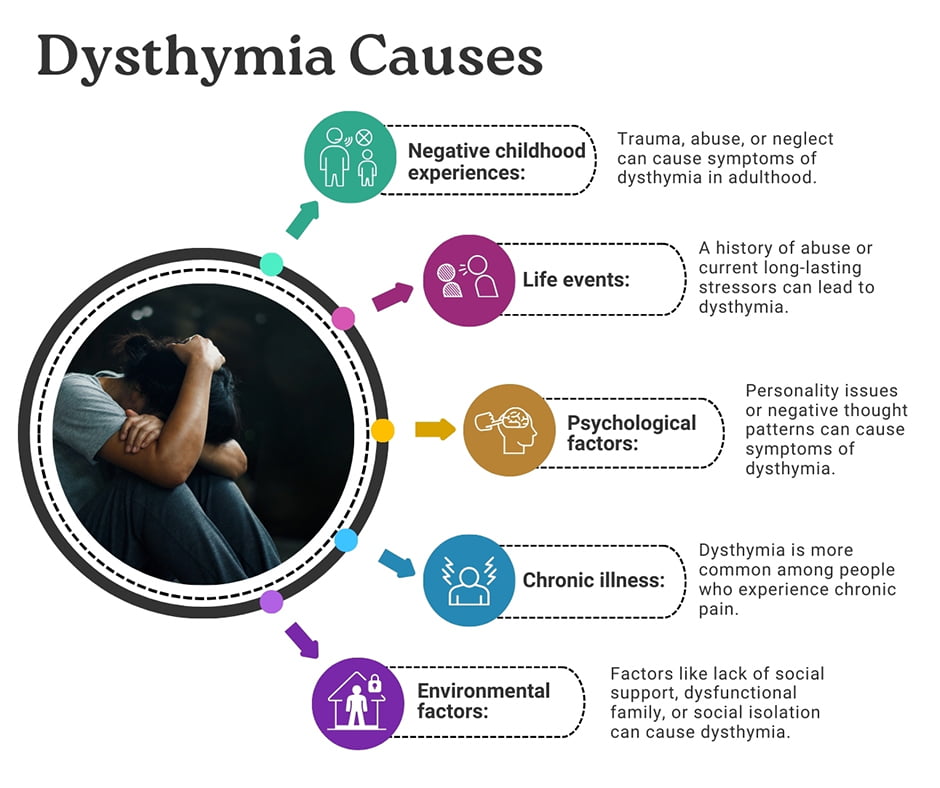
Dysthymia is caused by several factors including:
- Negative childhood experiences: Trauma, abuse, or neglect can cause symptoms of dysthymia in adulthood.
- Life events: A history of abuse or current long-lasting stressors can lead to dysthymia.
- Psychological factors: Personality issues or negative thought patterns can cause symptoms of dysthymia.
- Chronic illness: Dysthymia is more common among people who experience chronic pain.
- Environmental factors: Factors like lack of social support, dysfunctional family, or social isolation can cause dysthymia.
Dysthymia is a complex condition that is usually caused by a combination of different factors. Not everyone at risk for the disorder will develop it. However, it is important to remember there is treatment.
Is Dysthymia Common in the U.S.?
Dysthymia is a common condition with 2% of Americans living with the diagnosis. While dysthymia is not as well known as major depressive disorder (MDD), if left untreated, it can have significant impacts on an individual’s life. Treatment can greatly improve your quality and satisfaction with life.
Embrace Healing The Power of Trust in Therapeutic Relationships
“In my experience, the most effective aspect of therapy is the therapeutic relationship. Establishing trust between a client and clinician is the first step to healing.”
How Is Dysthymia Diagnosed?
Dysthymia can be diagnosed by a skilled trauma therapist. Your therapist will conduct an assessment and ask you questions about your history and past life experiences. The therapist will use the diagnostic criteria from the DSM-5 to help diagnose your condition.
How Is Dysthymia Treated?
Dysthymia can be treated with psychotherapy. Your specific treatment plan will depend on your personal preferences, the severity of your symptoms, and your therapist’s specialty.
Some options for treating dysthymia include:
- Psychotherapy: Talk therapies such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and rational emotive behavioral therapy (REBT) have been shown to help with symptoms of dysthymia.
- Medication: Research shows that medication has helped treat chronic depression, regardless of the brand.
- Combination therapy: For many individuals a combination of psychotherapy and medication works best.
- Social support: Support from family, friends, and loved ones is vital in the recovery of many disorders, dysthymia being one of them.
- Mindfulness and relaxation: Somatic regulation, or learning to relax the muscles in your body, can greatly improve mental health symptoms of dysthymia.
Oftentimes, the best treatment is a holistic approach that incorporates different treatments. Talk to your therapist about these options to find what works best for you.
What Medications Can Be Prescribed for Chronic Depression?
Some medications that are used to treat chronic depression include:
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs): These include Zoloft, Prozac, Lexapro, and Paxil, which all act to increase serotonin levels. Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that regulates mood, sleep, appetite, and pain sensation.
- Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs): These include Effexor and Cymbalta, which increase both serotonin and norepinephrine. Norepinephrine works on the fight-or-flight response. Increasing levels of neurotransmitters and hormones improve alertness, energy levels, and focus.
- Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs): Some examples of TCAs include Elavil and Tofranil. These medications work similarly to SNRIs by working on serotonin and norepinephrine but may have more side effects.
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs): Examples of these medications are Nardil and Parnate. MAOIs work by inhibiting the enzyme monoamine oxidase, which breaks down neurotransmitters like serotonin and norepinephrine.
- Atypical antidepressants: They are also known as Wellbutrin and Remeron and work by modulating dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin.
If you are considering medication for your dysthymia symptoms, talk to your psychiatrist about these different medications, as well as their side effects.
What Natural Treatments Can Help for Major Depressive Disorder?
Natural treatments can be highly effective for depression. A therapist or counselor can help you learn to naturally improve your depressive symptoms.
Some natural remedies for depression include:
- Physical activity: Any physical activity is good for our mental health. If making it to the gym is not realistic for your lifestyle, try riding a bike or walking to the store down the block instead of driving. Remember, any physical movement is good for your body and brain.
- Nutrition: Studies have shown that our gut is as important, if not more than our brain in controlling our moods. Be mindful of what you eat and make sure to include proteins, healthy fats, fruits, and vegetables in your daily diet.
- Sleep: Sleep plays a vital role in cell regeneration and mental health. Getting 7-9 hours nightly is important for most adults.
- Meditation: Mindfulness and meditation can help relieve stress. Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT) has been shown to decrease depression.
- Somatic regulation: Somatic regulation is learning to relax the muscles in your body. This can reduce stress and depression. Somatic regulation can be achieved through extending your exhale, progressive muscle relaxation, or other forms of relaxation using any of the five senses.
- Limit alcohol and caffeine: Decreasing your intake of these substances can improve your sleep, stabilize your mood, and improve depression.
All of these natural remedies for depression are excellent additions to evidence-based therapies. It is important to have both professional and social support in your depression recovery.
Where Can You Find Healthcare Providers for Depression Treatment?
You can find healthcare providers for depression in various ways including:
- Psychotherapists: A therapist is usually the first route in addressing and treating depression symptoms.
- Psychiatrists: Sometimes medication can help with depression treatment in conjunction with therapy.
You can find these healthcare providers by:
- Asking for a referral: You can ask your primary care physician (PCP) or ask friends or family members if they have received treatment for depression.
- Insurance: You can use your insurance website to find a healthcare provider who is covered by your insurance policy.
- Online platforms: You can search online platforms such as Psychology Today or SAMHSA to find a therapist.
Finding a therapist can be challenging, at times. However, the best way to find the right therapist for you is to start by meeting with someone and see if you feel comfortable working together.
How Long Does Therapy Last for Chronic Depression?
The duration of therapy is up to your willingness to participate in your treatment.
Some factors that may influence how long therapy lasts include:
- Response to therapy: Your progress and achievement of your treatment plan goals can dictate how long therapy takes.
- Your open-mindedness: How willing and open-minded you are in therapy will determine how long you want to participate in therapy.
- Preference: Some people wish to continue therapy to deal with day-to-day stressors, even after completing chronic depression therapy goals.
- Therapist approach: Different therapists may have their protocols for therapy, which may take different lengths of time.
However long therapy takes, we understand beginning therapy can be scary. It is important to take the first step to allow yourself the chance to change your life.
Does TMS Therapy for Depression Help With Chronic Pain?
TMS, or transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy is a form of treatment for depression. There has been some research on TMS for chronic pain, however, the results are not significant enough.
Do People With Chronic Depression Stay in Therapy for Life?
It is not necessary to stay in therapy for life if you have chronic depression or dysthymia. It is possible, however. The choice is up to you. Some people find it helpful to stay in therapy as stressful life events come up, or simply to process the events of the week after depression treatment is complete.
In the journey to overcome chronic depression, remember that effective treatment is within your reach. By choosing evidence-based approaches like REBT, CBT, and EMDR, you’re taking proactive steps towards a healthier mental state. Reach out to our experienced therapists today and embark on a path of healing and transformation.

